| 61.1. CTISIP resource | ||
|---|---|---|
 | Chapter 61. SIP - Session Initiation Protocol |  |
The Abilis SIP driver provides gateway functionalities between SIP and ISDN networks for audio services only; it isn't intended to support full SIP to SIP videoconferencing gateway. The Abilis SIP driver can be interfaced with:
Physical VolP telephones with SIP support;
Softphone program for PC;
PBX Digium Asterisk and other VoIP PBX with SIP support
For each of its SIP users ABILIS provides the choice of 4 possible operating modes, defined by the SIP-TYPE parameter.
SIP-TYPE can be specified as:
PHONE: to be used when connecting SIP
phones to Abilis;
SERVER: to be used when Abilis has to
emulate a SIP phone;
LOCAL-PEER: to be used with a SIP gateway
when the SIP-DOMAIN is owned by the
Abilis;
REMOTE-PEER: to be used with a SIP gateway
when the SIP-DOMAIN is owned by the SIP
gateway.
NNI: for SIP trunk interconnection as per
ST-769 specification (network-network-interconnection).
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Many of the other SIP configuration parameters, like SIP-DOMAIN, are to be specified
depending to the |
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The user may also be a PEER, it means a device that has the same SIP role of the Abilis and the calling number has to be passed unchanged. |
The SIP registration process looks something like this:
Registration is the process in which the endpoint sends a SIP REGISTER message to the SIP SERVER to let it know where it is. The second REGISTER contains an Authorization header, what contains the SIP user and the password.
On Abilis, depending of SIP-TYPE parameter the registration can be:
Local: the endpoint will register on
Abilis. The USER and PWD
parameters of Abilis are used for registration.
Remote: the Abilis will register on SIP
server. The SIP-REM-USER,
SIP-REM-AUTH-USER and
SIP-REM-PASS parameters of Abilis are used for
registration.
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
To enable remote registration, the SIP-REM-REG parameter must be enabled. |
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The SIP-REM-AUTH-USER
must be configured only if SIP authentication user is different
from SIP user. By default the |
If the SIP-TYPE: PHONE
usually the registration is Local, the
SIP phone registers itself on Abilis. The SIP-HOST
and/or SIP-UDP-REMPORT must be dynamic.
For SIP-TYPE: LOCAL-PEER if
the SIP-HOST and/or
SIP-UDP-REMPORT are dynamic then the endpoint must
register itself on Abilis, in order that the Abilis can find the IP
address of the endpoint.
For SIP-TYPE: SERVER or
SIP-TYPE:REMOTE-PEER usually the
registration is Remote, the Abilis
register itself on SIP server.
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapter: Section 87.4.16, “How to troubleshoot SIP registration problems”. |
Examples of basic configuration of SIP user to interconnect with Abilis for each SIP-TYPE:
PHONE

[08:23:09] ABILIS_CPX:a user:sip_phone pwd:sip_phone sip:yes sip-type:phone sip-host:dynamic sip-number:555
COMMAND EXECUTED
LOCAL-PEER
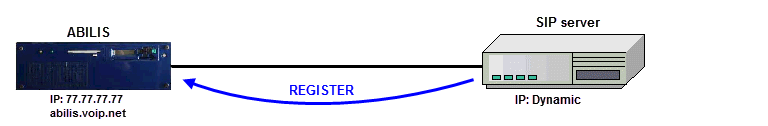
[08:27:09] ABILIS_CPX:a user:sip_peer pwd:sip_peer_pwd sip:yes sip-type:local-peer sip-domain:abilis.voip.net sip-host:dynamic sip-maxses-bid:20 sip-number:*
COMMAND EXECUTED ![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapter: Section 61.5.2, “Example: Abilis and a SIP server registered in Abilis domain (SIP-TYPE:LOCAL-PEER)”. |
SERVER
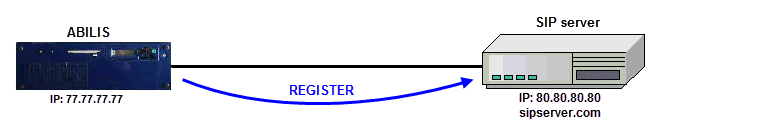
[08:30:09] ABILIS_CPX:a user:voipclient pwd:swordfish sip:yes sip-type:server sip-domain:sipserver.com sip-host:80.80.80.80 sip-maxses-bid:20 sip-number:*COMMAND EXECUTED [08:31:09] ABILIS_CPX:s user:voipclient sip-rem-reg:yes sip-rem-user:voipclient sip-rem-pass:swordfishCOMMAND EXECUTED
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The SIP-MAXSES-BID parameter is the maximum number of SIP bidirectional sessions. |
REMOTE-PEER

[08:30:09] ABILIS_CPX:a user:voippeer pwd:swordfish sip:yes sip-type:remote-peer sip-domain:sipserver.com sip-host:80.80.80.80 sip-maxses-bid:20 sip-number:*COMMAND EXECUTED [08:31:09] ABILIS_CPX:s user:voippeer sip-rem-reg:yes sip-rem-user:voippeer sip-rem-pass:swordfishCOMMAND EXECUTED
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
To check if SIP users are registered, type the following command:
[11:04:10] ABILIS_CPX:d ctisip registry
User Host Port REG LIFETIME AGE
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
voipclient 080.080.080.080 5060 REMOTE 240 9
sip_peer 192.168.020.104 46022 LOCAL 120 112
sip_phone 192.168.020.107 56125 LOCAL 120 112In this example, the SIP user voipclient is
registered to the remote peer with IP address: 80.80.80.80. SIP users
sip_peer and sip_phone are
registered to Abilis.
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapters: Section 61.7.5, “Debug of the CTISIP resource”; Section 87.4.16, “How to troubleshoot SIP registration problems”. |
The SIP devices can communicate also without SIP Registration,
only if the devices are on the same LAN or both are on static public
IPs. In this case, SIP-HOST and
SIP-UDP-REMPORT must be configured, not
dynamic.

![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
To disable remote registration, the
|
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
If Abilis has more IP addresses, then SIP-SRCADD parameter must be configured with a corresponding source IP address. |
Example of configuration of SIP user to comunicate without registration:
[08:30:09] ABILIS_CPX:a user:sip_no_reg sip:yes sip-type:remote-peer sip-domain:sipserver.com sip-host:80.80.80.80 sip-srcadd:77.77.77.77 sip-udp-remport:5060COMMAND EXECUTED [08:31:09] ABILIS_CPX:s user:sip_no_reg sip-maxses-bid:20 sip-number:* sip-rem-reg:noCOMMAND EXECUTED
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The SIP-MAXSES-BID parameter is the maximum number of SIP bidirectional sessions. |
A caller sends this message (INVITE) to request that another endpoint join a SIP session, such as a conference or a call. This message can also be sent during a call to change session parameters.
Meaning of the most important parameters:
Request-URI: The
Request-URI header field contains the URI
of the next hop of the message.
From: The From header
field identify the initiator of the invitation
To: The To header field
identify the recipient of the invitation
These parameters change depending on the SIP-TYPE parameter.
Below we see the differences between the INVITE message for each
SIP-TYPE:
If SIP-TYPE:PHONE the INVITE
from 101 to the user sent by the Abilis contains:
Request-Uri:
test@80.80.80.80 (where
test is the SIP user and
80.80.80.80 is the IP address of the
device)
From:
101@abilis.voip.net (where
abilis.voip.net is the local domain of
the Abilis)
To:
test@abilis.voip.net
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the
|
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapters: Section 61.4, “Connecting Abilis and a SIP phone”; Section 84.9, “How to register a SIP telephone onto Abilis”. |
If SIP-TYPE:LOCAL-PEER the
INVITE from 101 to 0123456 sent by the Abilis contains:
Request-Uri:
0123456@80.80.80.80 (where
0123456 is the called number and
80.80.80.80 is the IP address of the
user)
From:
101@abilis.voip.net (where
abilis.voip.net is the local domain of
the Abilis)
To:
0123456@80.80.80.80
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the
|
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the |
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapter: Section 61.5.2, “Example: Abilis and a SIP server registered in Abilis domain (SIP-TYPE:LOCAL-PEER)”. |
If SIP-TYPE:SERVER the
INVITE to 0123456 sent by the Abilis contains:
Request-Uri:
0123456@sipserver.com (where
0123456 is the called number and
sipserver.com is the FQDN
of the server)
From:
abilis@sipserver.com (where
abilis is the SIP remote user and
sipserver.com is the remote
domain)
To:
0123456@sipserver.com
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the
|
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapters: Section 61.5.3, “Example: Server and Abilis registered in Server remote domain (SIP-TYPE:SERVER)”; Section 84.11, “How to register Abilis as a client of a SIP server”. |
If SIP-TYPE:REMOTE-PEER the
INVITE from 101 to 0123456 sent by the Abilis contains:
Request-Uri:
0123456@sipserver.com (where
0123456 is the called number and
sipserver.com is the FQDN
of the remote peer)
From: 101@77.77.77.7
(where 77.77.77.77 is the
IP address of the Abilis)
To:
0123456@sipserver.com
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the
|
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the |
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapter: Section 61.5.4, “Example: Server and Abilis registered in Server remote domain (SIP-TYPE:REMOTE-PEER)”. |
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapter: Section 82.32.1, “How to trace only the SIP traffic”. |
Add the resource to the Abilis system with the following command.
[09:08:14] ABILIS_CPX:a res:ctisip
RES:CTISIP ALREADY EXISTSThe CTISIP resource may already exist in the system, but may not yet be active: set it active with the command:
[09:10:00] ABILIS_CPX:s act res:ctisip
COMMAND EXECUTED![[Caution]](../images/caution.png) | Caution |
|---|---|
After adding or setting the CTISIP active, you must restart the Abilis to make the resource running (use the command warm start to reboot the Abilis). |
[11:01:39] ABILIS_CPX:s p ctisip act:yes
COMMAND EXECUTED![[Caution]](../images/caution.png) | Caution |
|---|---|
Execute the initialization command init res:ctisip to activate the changes made on the upper case parameters. Use the command save conf and restart Abilis (i.e. With warm start command) to set act the changes made on the lowercase parameters. |
Use the command d p ctisip to show the parameters of the resource and use the command d p ctisip ? to display the meaning of the parameters.
[11:02:19] ABILIS_CPX:d p ctisip
RES:CtiSip --------------------------------------------------------------------
Run DESCR:Session_Initiation_Protocol
LOG:NO ACT:YES TRACE:SIP
siplog:ERR siplogsize:200
sesnum:30 non-invite-sesnum:50 max-sub:100
wdir:C:\APP\SIP\
-- IP settings and filters ---------------------------------------------
LOCPORT-BASE:5060 RTP-PORT-BASE:6000 SIP-TOS:0-N
LOCPORT-RANGE:100 rtp-port-range:110 RTP-TOS:0-D
LOCPORT:5060 mxps:2172
SRCADD:OUT-IP
EXTERNAL-IP:OUT-IP
IPSRC:* IPSRCLIST:#
-- Sip signalling ------------------------------------------------------
DOMAIN:
UA:AUTO (Abilis CPX - Ver. 8.9.0/STD - Build 4665.39 - Branch 8.9)
LOC-REG-EXPIRY:120 QUALIFY:15 AUTH-TOUT:4
LOC-SUB-EXPIRY:180 KEEPALIVE:90 AUTH-TOUT-INVITE:4
MAX-NNI-FWD:2 CPO-SIGNALLING:NO T1:500 T2:4 T4:5
-- RTP Audio codecs and Fax --------------------------------------------
CPO-RTP:NO DTMF-MODE:RFC2833 T38:YES
CHAN-FREQ:20 DTMF-PLAY:100 T38-G711:NO
DISC-AUDIO:NO DTMF-SILENCE:100 T38-PACKING:1
RTP-REORDER:0 DTMF-DETECT-PLAY:40 T38-REDUND:REDUNDANCY
T38-REORDER:0 DTMF-DETECT-SILENCE:40 T38-REDUND-PCK:1
-- Ctir signalling -----------------------------------------------------
ROUTING:EN-BLOC ROUTE-BY-SD:NO CLIP-RULE:PRIVATE
DIALT:5 PROVIDE-SG:NO CTIP-TYPE:USER
T302:15 RG-IN:DISABLE NPOO-CT:SYS (NO) Meaning of the most important parameters:
LOGLogging functionalities activation/deactivation.
ACTRuntime CTISIP activation/deactivation
[NO, YES].
TRACETraced data [SIP,
ALL], where:
SIP: trace only SIP
ALL: trace SIP and RTP.
siplogLog events filter at system startup [ERR,
REG, INFO] or
FULL, where:
ERR, REG,
INFO filters can be joined using ','
(comma);
FULL: means every type of
event.
siplogsizeLog size [20..2000 Kibyte].
mxpsUDP payload [1472..65507 byte].
sesnumThe maximum number of SIP sessions available for phone calls [1..255].
non-invite-sesnumNumber of SIP sessions/dialogs initiated by NON-INVITE methods: i.e. Register, Subscribe and Notify [30..100].
udp-locportLocal UDP port of SIP protocol [1..65535].
UDP-PORT-BASEBase local UDP port usable for RTP/RTCP sessions [1024..65535]; this feature is required to assign high priority to RTP/RTCP packets.
UDP-PORT-RANGERange of permitted local UDP ports usable for RTP/RTCP
sessions [50..1000]; this value must not be lower than
(sesnum * 2 + 50).
SIP-TOSSets the TOS value for SIP protocol.
RTP-TOSSets the TOS value for RTP protocol.
SRCADDSource IP address for outgoing connections
[R-ID: the source IP address of the outgoing
datagrams will be set to the current RouterID value;
OUT-IP: the source IP address of the outgoing
datagrams will be set on the base of the output IP interface;
1-126.x.x.x, 128-223.x.x.x: the source IP
address of the outgoing datagrams will be set to the selected
value; Ip-nnn: use the current
IPADD of the specified IP resource].
EXTERNAL-IPAbilis external IP address. [R-ID: the
source IP address of the outgoing datagrams will be set to the
current RouterID value; OUT-IP: the source IP
address of the outgoing datagrams will be set on the base of the
output IP interface; 1-126.x.x.x,
128-223.x.x.x: the source IP address of the outgoing
datagrams will be set to the selected value]. When
OUT-IP or R-ID are set, the
address must be determined at the call start and must not change
until call end.
DISPLAY-NAMESelects how to fill Display Name in From,
P-Asserted-Identity, Remote-Party-ID fields
[NO: Do not add display name;
CG: the value present in the
CG field (calling number) provided by CTIR;
SG: the value present in the
SG field (subaddress calling) provided by CTIR;
SG-CG: the value present in the
SG field or CG field if
SG field is missing;
ADDRBOOK: field with the name of calling number
from address book; ADDRBOOK-SG: field with
calling number if the name of calling number is missing in address
book].
![[Note]](../images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
When |
IPSRCIncoming requests: accepted source IP address [*,
1-126.x.x.x, 127.0.0.1, 128-223.x.x.x]; a client is accepted if it
also satisfies SIP-IP-PERMIT specified in User
table.
IPSRCLISTIncoming requests: list of further accepted source
IP addresses [#, IP/IR/RU/MR listname]; a client is accepted if it
also satisfies SIP-IP-PERMIT specified in User
table.
LOC-SUB-EXPIRYExpiration time of incoming subscriptions [60..3600 sec].
max-subMaximum number of subscriptions that CTISIP may handle
independently from the event type, the subscriber and the
monitored resource [0..1000]. If we are handling two SIP phones
with BLF and one
phone monitors 150 phones and the other monitors 50 phones then
max-sub is 150+50=200. If we have 30 phones and
each monitors 20 phones, then we have 600 subscriptions.
AUTHAuthentication types offered to autenticating/registering
users (incoming calls/registrations) [PLAIN,
DIGEST]. Values can be joined using ','
character.
REM-AUTHAuthentication types acceptable when
authenticating/registering to a peer (outgoing
calls/registrations).[PLAIN,
DIGEST]. Values can be joined using ','
character.
LOC-REG-EXPIRYDefault duration of incoming registration; users must register themselves before this time interval expires.
QUALIFYQualify time interval [4..300 sec].
MAX-NNI-FWDMaximal number of redirections (forwards) between two NNI users [1..10].
AUTH-TOUTSIP NOT-INVITE authentication timeout for incoming/outgoing calls initiated by REGISTER method [2..255 sec].
AUTH-TOUT-INVITESIP INVITE authentication timeout for incoming/outgoing calls initiated by INVITE method [2..255 sec].
KEEPALIVESession keepalive time [90..600 sec]; when this session inactivity timer expires a RE-INVITE or UPDATE message is sent. The keepalive during a call is used to monitor if the connection is stil alive.
CTIP-TYPECTIP type assigned to CTISIP driver
[USER, NET-PRIVATE,
NET-PUBLIC].
NPOO-CTEnable/disable Net-Public to Net-Public call transfer when
both calls are outgoing (outgoing to outgoing)
[NO: NP to NP disabled; YES:
NP to NP enabled, except when both calls are outgoing, which is
not allowed to avoid the “hang trunk” problem;
SYS: NP to NP depends on NP-CT in
CtiSys].
ROUTINGRouting management
[PREFIX, EN-BLOC].
DIALTDialing timeout [1..15 sec]. When SIP resource is the destination and at least a number was already submitted the timeout between digits is 5 seconds (DIALT) but may be changed.
T302Timeout for “empty” setup [15..120 sec].
ROUTE-BY-SDIt allows routing using subaddress called field (SD)
[NO: the SD is completely ignored;
YES: the user corresponding to SD is searched:
if found the call is forwarded to that user, otherwise the
standard search in CTISIP table is performed;
USER: the user corresponding to SD is searched:
if found and the user has parameter
SIP-ROUTE-BY-SD:YES, the
call is forwarded to that user, otherwise the standard search in
CTISIP table is performed].
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
Interesting chapter: Section 61.4.4.2, “Abilis CTI Routing of “Site 1 ” using subaddress called field”. |
PROVIDE-SGAllows insertion of SIP USER NAME in subaddress calling
field [NO: disable insertion of USERNAME in
calling subaddress; YES: enable insertion of
USERNAME in calling subaddress; USER: insertion
of USERNAME in calling subaddress depends on individual user
configuration]. When it's enabled, either as result of value
YES or because value is USER
and the user corresponing to the subaddress content allows it, the
call sent to CTIR will include in the subaddress calling field the
SIP USER NAME of the caller.
DTMF-MODEDTMF mode used by CTISIP in outgoing DTMF
[INBAND: the outband DTMF received from CTIR is
not dropped, only the audio stream is passed;
INFO: the outband DTMF received from CTIR is
sent using INFO message; RFC2833: the outband
DTMF received from CTIR is sent using RFC2833 payload].
DISC-AUDIOEnable/Disable the reproduction of the audio message present
in DISCONNECT with in-band-info received from CTIR
[NO, YES]. If set ot
YES the duration of the SIP session in active
state is increased until CTIR times-out (typically up to 30 sec),
or the SIP agent closes the call.
PLAY-DTMFDuration of a DTMF played from a DTMF FULL FRAME [40..1000 msec]. When CTISIP has to convert a DTMF FULL FRAME command to CTIR DTMF frame, it produces as many frames as needed to cover the period specified by this parameter. The actual interval must be rounded to the value immediately higher than configured one.
PLAY-SILENCEDuration of a silence played after a
PLAY-DTMF [50..1000 msec]. When CTISIP has to
convert a DTMF FULL FRAME command to CTIR DTMF frame, it produces
as many frames as needed to cover the perios specified by
PLAY-DTMF parameter. Before a new DTMF can be
played, a silence period must elapse, and this is controlled by
this parameter.
DETECT-DTMFDuration of a DTMF from CTIR in order to allow digit recognition [20..100 msec]. When CTISIP received DTMF frames from CTIR, and after it created the most accurate and monotonical timestamp, the DTMF length is measured and for a successful digit recognition it must be of at least the length specified here. If the configured value is not an exact multiple of the frame rate, it must be rounded to the next upper value multiple of frame rate.
DETECT-SILENCEDuration of a silence after a DTMF from CTIR in order to recognise a digit [20..100 msec].When receiving DTMFs from CTIR to SIP this is the minimum duration of the silence after a tone to actually recognize the following tone and digit to be sent to SIP.
T1SIP T1 time; Round Trip Time (RTT) estimate.
T2SIP T2 time; maximum retransmission interval for NON-INVITE requests and INVITE responses.
T4SIP T4 time; maximum duration that a message can remain in the network.
CHAN-FREQDesired channel frequency for bandwidth optimisation, to be rounded down to a codec frame length multiple [20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 msec]. It represents how many msec of voice are desired to be packed into a single UDP packet; it's a “desire” in the sense that the actual optimisation will depend on the frame length in msec of the coder in use, and the result will be an a approximation by defect.C
Enables/disables Call Path Optimization between two SIP
users. It is used when
SIP-CPO:SYS in user service,
otherwise the value of SIP-CPO is used.
CPO-SIGNALLINGCall Path Optimization signalling [NO:
never attempt a CPO of the signalling path;
TRANSFER: attempt the CPO just in case of
transferring; ALWAYS: always attempt the CPO
between two SIP call legs]
DOMAINDomain for local users. From 0 up to 64 characters in the range ['0'..'9', 'a'..'z', '-', '.']. DN name is forced to lower case. If Abilis has clients in the public side you can also specify a FQDN.
CLIP-RULESpecifies the threatment of the CG number for calls TO the
SIP users (OUTGOING) [PRIVATE,
PUBLIC]. If PRIVATE the CG
is sent unmodified, if PUBLIC the CG is emptied
when PI is set to RESTRICTED.
RG-INEnable/disable management of incoming redirecting
[DISABLE, ENABLE].
T38Enable/disable T.38 support [NO,
YES].
T38-PACKINGNumber of T.38 packets in UDP packet [1..4].
T38-REDUNDError recovery method [NONE,
REDUNDANCY: if the redundancy method is used
it's possible to increase the redundancy packets].
T38-REDUND-PCKNumber of T.38 packets used for error recovery [1..4].
T38-G711Enable/disable T.38 support with G.711 codec
[NO, YES].
RCC-DISABLEEnable/disable Runtime Codec Change (RCC)
[NO, YES]. This feature
permits the change of the coder once the call is already
established. The purpose of this feature, which is perfectly SIP
compliant, is to avoid transcoding all the times that it is
possible by choosing a coder which is supported by both sides
although not currently in use. This feature is very effective when
call transfers takes place. A user may have two calls with two
different parties that use two different codec, e.g. G.711 and
G.729, when a call transfer is ordered the two parties will be
directly connected but since one party was using G.711 and the
other G.729 we were forced to make a transcoding even if both
supports G.729. With the RCC feature the party running G.711 will
be changed on the fly to G.729. The run time codec change allows
to save voice quality and sw and hw resource in case of
transcoding. Disable the RCC only if the SIP devices have troubles
in handling the codec change.
UALocal user agent. AUTO or from 1 up to 32
ASCII printable characters. Case is preserved. Spaces are allowed.
Strings holding spaces must be written between quotation marks
(E.g.: "my user agent"). Abilis may present itself as a different
device, it's useful to avoid filters based on User Agent.
wdirWorking directory where persistent information is stored. It cannot be empty. Physical full path in DOS notation, i.e. starting with a drive letter in the range ['A'..'Z'] and ending with the '\' character. Max. 128 characters. Case is preserved. Spaces are allowed. Strings holding spaces must be written between quotation marks (E.g.: "C:\My dir\").
The following command allows the administrator to change the configuration of the resource:
s p ctisip parameter:value...
![[Caution]](../images/caution.png) | Caution |
|---|---|
To activate the changes made on the upper case parameters, execute the initialization command init res:ctisip; while to set act the changes made on the lowercase parameters a save conf and an Abilis restart are required (i.e. With warm start command). |